Biosensors in environmental monitoring
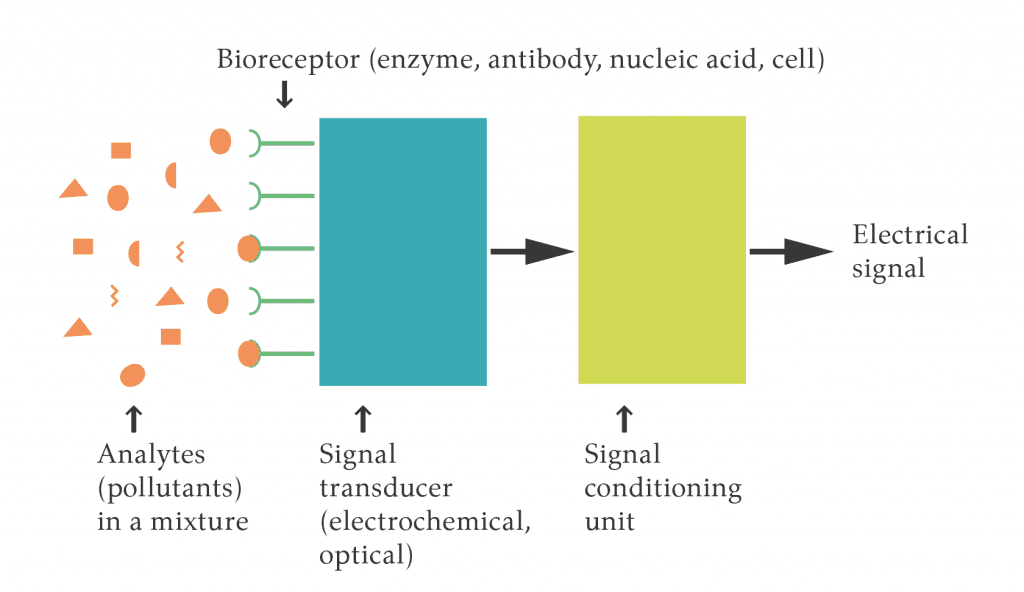
A biosensor (biological sensor) works fundamentally by detecting the presence of chemicals. It uses a living organism or biological molecules (e.g., enzymes, antibodies) to bind variables of interest and a transducer to generate an electrical signal proportional to the resulting change in analyte concentration. In other words, it is a device that converts biological processes into a detectable electrical signal. A typical biosensor is shown in Figure 1, which consists of the following components:
Biosensors in environmental monitoring Read More »